Environmental crisis is a pressing issue that affects the entire world. The degradation of natural resources, pollution, and climate change are some of the key factors contributing to this crisis. The effects of environmental crisis can be seen in various forms such as extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity, and health problems. It is a complex and multifaceted problem that requires global attention and action.
The world is currently facing a critical environmental crisis, which includes issues such as deforestation, ocean acidification, and air pollution. These problems have significant impacts on ecosystems, human health, and the economy. The degradation of natural habitats and the loss of biodiversity are particularly concerning, as they can lead to long-term negative consequences for the planet. Additionally, the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events are clear signs of the environmental crisis we are facing.
1. Deforestation: Impact on Biodiversity and Climate
Deforestation is the process of clearing, destroying, or otherwise removing a forest or stand of trees. This practice has a significant impact on biodiversity and climate. When forests are cleared, countless species of plants and animals lose their habitats, leading to a loss of biodiversity. Additionally, trees play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation disrupts this process, leading to an increase in greenhouse gases and contributing to climate change.
Furthermore, deforestation can lead to soil erosion, altered water cycles, and an increase in the frequency and severity of natural disasters such as floods and landslides. The effects of deforestation are not limited to the areas where it occurs; they can have far-reaching consequences for the entire planet. Efforts to combat deforestation include reforestation initiatives, sustainable logging practices, and the protection of existing forested areas.
2. Ocean Pollution: Threats to Marine Life and Human Health
Ocean pollution, caused by various sources such as plastic waste, chemical runoff, and oil spills, poses significant threats to marine life and human health. Plastic pollution, for example, can entangle and suffocate marine animals, as well as leach harmful chemicals into the water. Additionally, the ingestion of plastic by marine animals can have deadly consequences, and the presence of plastic particles in the food chain can ultimately impact human health.
Chemical runoff from agricultural and industrial activities can lead to algal blooms and dead zones, where oxygen levels are depleted, making it difficult for marine life to survive. Oil spills, whether from industrial accidents or deliberate discharge, can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems, causing long-term damage to habitats and populations. Efforts to address ocean pollution include the development of biodegradable materials, stricter regulations on waste disposal, and cleanup initiatives to remove existing pollution from the oceans.
3. Air Pollution: Impact on Human Health and the Environment
Air pollution, caused by emissions from vehicles, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels, has significant impacts on human health and the environment. Inhaling polluted air can lead to a variety of health problems, including respiratory issues, heart disease, and even premature death. Additionally, air pollution can damage crops and forests, leading to a decrease in agricultural productivity and biodiversity loss.
Air pollution also contributes to the formation of smog and acid rain, which can have detrimental effects on ecosystems, water quality, and infrastructure. Efforts to combat air pollution include the development of cleaner energy sources, the implementation of emission control technologies, and the promotion of public transportation and other alternatives to driving. Additionally, international cooperation is crucial to address transboundary air pollution that affects multiple countries.
4. Water Scarcity: Impacts on Agriculture and Access to Clean Water
Water scarcity, caused by factors such as overuse, pollution, and climate change, has significant impacts on agriculture and access to clean water. In many regions, water scarcity leads to reduced crop yields and agricultural productivity, threatening food security for communities and nations. Additionally, competition for limited water resources can lead to conflicts and social instability.
Furthermore, water scarcity affects the ability of communities to access clean and safe drinking water, leading to a range of health issues and perpetuating the cycle of poverty. Climate change exacerbates water scarcity by altering precipitation patterns and increasing the frequency of droughts and floods. Efforts to address water scarcity include sustainable water management practices, investment in water-saving technologies, and the protection of watersheds and wetlands to preserve water sources.
5. Loss of Biodiversity: Ecological and Economic Implications
The loss of biodiversity, driven by factors such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, has significant ecological and economic implications. Biodiversity is essential for the healthy functioning of ecosystems, providing services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control. The loss of biodiversity can disrupt these services, leading to reduced agricultural productivity and increased vulnerability to invasive species and diseases.
Additionally, biodiversity loss can have economic impacts, as many industries rely on natural resources and biological diversity for their livelihoods. For example, the decline of fish populations due to overfishing can threaten the food security and economic stability of coastal communities. Efforts to address the loss of biodiversity include the establishment of protected areas, the enforcement of regulations to prevent overexploitation of natural resources, and the promotion of sustainable land and resource management practices.
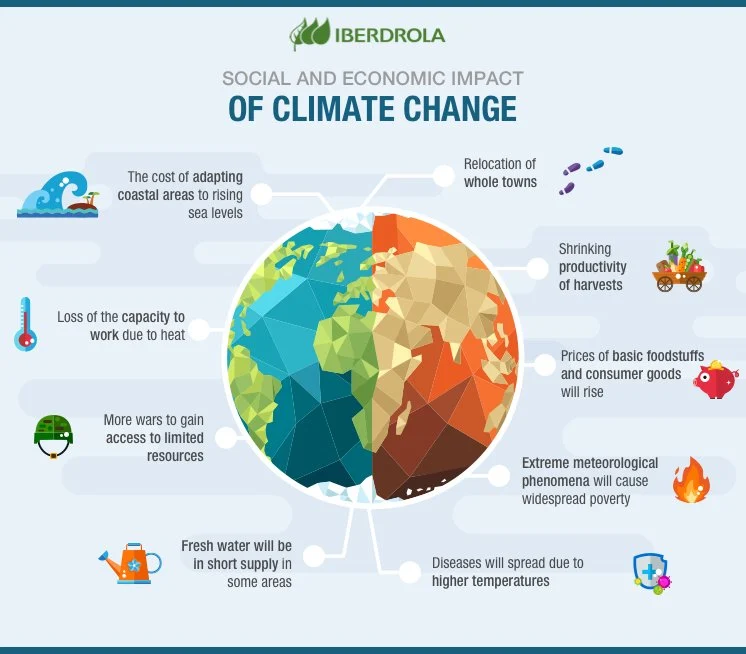
6. Climate Change: Rising Temperatures and Extreme Weather Events
Climate change, driven by factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and industrial activities, is leading to rising global temperatures and an increase in extreme weather events. These changes have significant impacts on ecosystems, human communities, and the global economy. Rising temperatures can lead to the loss of polar ice, rising sea levels, and the acidification of oceans, threatening marine life and coastal communities.
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, can lead to loss of life, destruction of infrastructure, and disruptions to food and water supplies. Climate change also exacerbates existing social and environmental challenges, such as poverty, food insecurity, and migration. Efforts to address climate change include the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, the promotion of renewable energy sources, and international agreements to limit global temperature rise.
7. Natural Disasters: Impact on Communities and Infrastructure
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and wildfires, have significant impacts on communities and infrastructure, leading to loss of life, displacement of populations, and economic damage. Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of some natural disasters, exacerbating their impacts. For example, rising sea levels and changing precipitation patterns can lead to more frequent and severe flooding in coastal and inland areas.
Additionally, deforestation and land use changes can exacerbate the impacts of natural disasters, such as landslides and soil erosion. The effects of natural disasters are often felt most acutely by marginalized and vulnerable communities, who may have limited resources to prepare for and recover from these events. Efforts to address the impacts of natural disasters include early warning systems, disaster preparedness and response plans, and the implementation of resilient infrastructure and building codes.
8. Waste Management: Environmental and Public Health Concerns
Waste management, including the disposal and treatment of solid and hazardous waste, presents significant environmental and public health concerns. Improper waste disposal can lead to pollution of soil, water, and air, as well as the spread of diseases through contaminated water and food. Additionally, the accumulation of plastic and electronic waste poses long-term challenges for ecosystems and human health.
Efforts to improve waste management include the development of recycling and waste reduction programs, the implementation of proper disposal and treatment facilities, and public education initiatives to raise awareness about the impacts of improper waste management. Additionally, the concept of a circular economy, which aims to minimize waste and maximize the reuse and recycling of materials, is gaining traction as a sustainable approach to waste management.
| Environmental Crisis | Effects |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, disruption of water cycle |
| Air Pollution | Respiratory diseases, acid rain, global warming |
| Water Pollution | Contaminated drinking water, marine life destruction |
| Climate Change | Extreme weather events, rising sea levels, food and water shortages |
SONUÇ
Environmental crisis, such as deforestation, air and water pollution, and climate change, have severe effects on the planet and its inhabitants. Loss of biodiversity, respiratory diseases, and extreme weather events are just a few examples of the widespread impact of these crises. It is crucial for individuals, communities, and governments to take action to address and mitigate these environmental challenges.