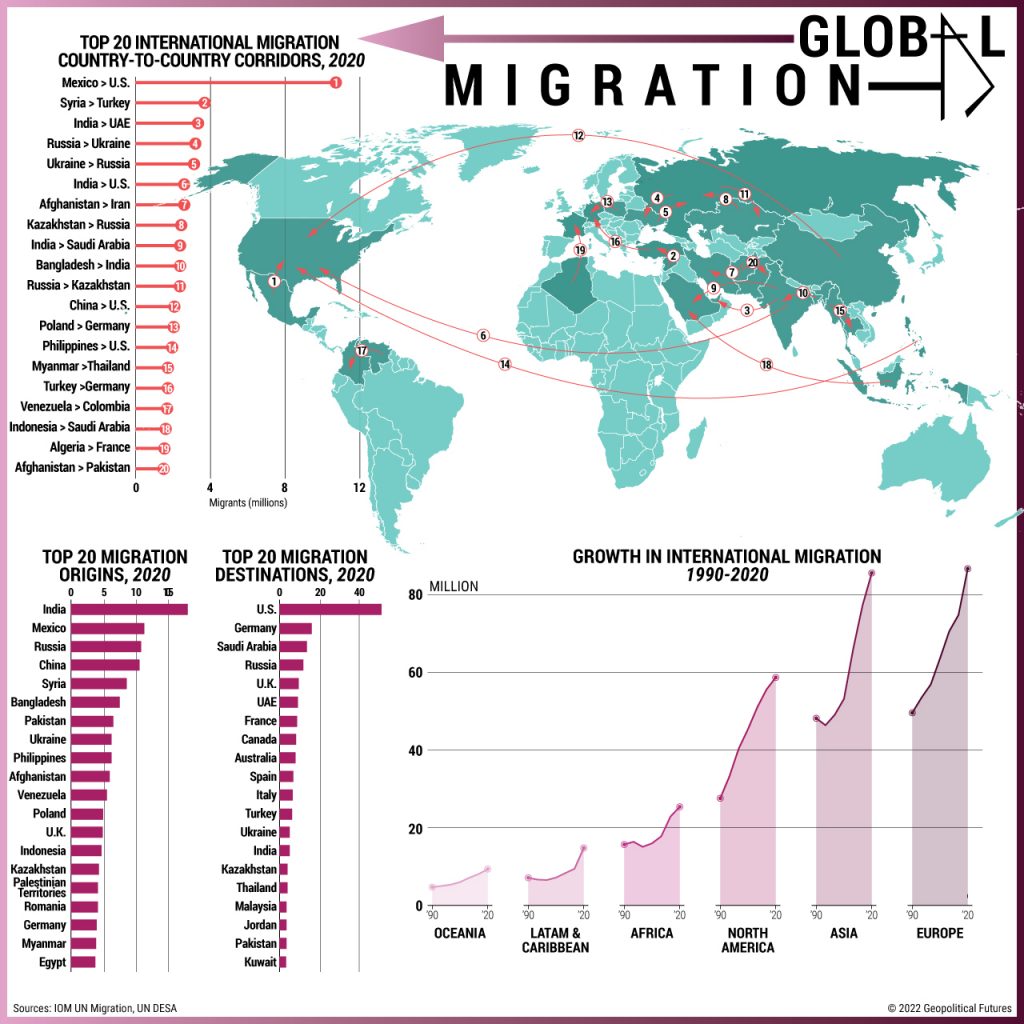
In recent years, the world has witnessed significant shifts in migration patterns, leading to profound changes in demographics across various regions. Understanding how global migration trends are shaping demographics is crucial for grasping the complexities of modern societies. As people move across borders in search of better opportunities, safety, and quality of life, the implications of these trends extend beyond mere numbers. They influence cultural dynamics, economic growth, and social structures, making it essential to explore this topic in depth.
This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of global migration, examining the driving forces behind these trends and their impact on both origin and destination countries. Readers will discover how migration affects population diversity, labor markets, and even public policy. Furthermore, we will analyze the role of technology and globalization in facilitating migration, as well as the challenges and opportunities that arise from these demographic shifts.
As we navigate through the complexities of migration, we invite you to join us on this enlightening journey. By understanding how global migration trends are shaping demographics, you will gain valuable insights into the future of societies worldwide. Stay with us as we uncover the stories behind the statistics and explore the human experiences that define this global phenomenon.
Global migration trends have a profound impact on demographics, influencing population structures, cultural dynamics, and economic landscapes across the world. Understanding these trends is essential for policymakers, businesses, and communities as they navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing global environment.
The Rise of Urbanization
Urbanization is one of the most significant outcomes of global migration trends. As people move from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities, urban centers are experiencing unprecedented growth. This shift not only alters the demographic makeup of cities but also places immense pressure on infrastructure, housing, and public services.
In many developing countries, urban migration is driven by factors such as poverty, lack of employment opportunities, and environmental changes. As a result, cities are becoming melting pots of cultures, leading to increased diversity but also potential social tensions. Policymakers must address these challenges to ensure sustainable urban development.
Aging Populations and Labor Shortages
Many developed countries are facing aging populations due to low birth rates and increased life expectancy. This demographic shift creates labor shortages, prompting nations to look towards immigration as a solution. Migrants often fill essential roles in various sectors, from healthcare to agriculture, helping to sustain economic growth.
However, the integration of migrants into the workforce presents challenges, including language barriers and cultural differences. Effective policies and programs are necessary to facilitate the smooth transition of migrants into the labor market, ensuring that both the economy and the migrants themselves benefit from this dynamic.
Refugee Crises and Humanitarian Responses
Global migration trends are also shaped by forced displacement due to conflict, persecution, and environmental disasters. Refugee crises have become a pressing issue, with millions of people seeking safety and stability in other countries. This influx of refugees significantly impacts the demographics of host nations, often leading to increased diversity but also potential strain on resources.
Humanitarian responses to these crises are critical. Countries must balance the need to provide assistance and protection to refugees while addressing the concerns of their own citizens. Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, and international organizations are essential to create effective solutions that benefit both refugees and host communities.
Economic Impacts of Migration
Migration has profound economic implications for both sending and receiving countries. Remittances sent back home by migrants contribute significantly to the economies of their countries of origin, often providing essential support for families and communities. Conversely, receiving countries benefit from the skills and labor that migrants bring, which can stimulate economic growth.
However, the economic impact of migration is not uniformly positive. Concerns about job competition and wage suppression can lead to social tensions. Policymakers must carefully consider the economic dynamics of migration to create policies that maximize benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Cultural Exchange and Integration
Migration fosters cultural exchange, enriching societies with diverse traditions, languages, and perspectives. This cultural diversity can enhance creativity and innovation, contributing to a more vibrant social fabric. However, the integration of migrants into host societies can be challenging, requiring efforts to promote understanding and acceptance.
Successful integration involves not only economic participation but also social inclusion. Programs that encourage cultural exchange, language learning, and community engagement can help bridge gaps between migrants and local populations, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual respect.
Policy Responses to Migration Trends
Governments around the world are grappling with how to respond to changing migration patterns. Policies can range from open-door immigration strategies to strict border controls. The effectiveness of these policies often depends on the specific demographic and economic contexts of each country.
Comprehensive immigration policies that address labor market needs, humanitarian obligations, and social integration are essential. Policymakers must engage with various stakeholders, including businesses, community organizations, and migrants themselves, to develop solutions that are both effective and equitable.
The Role of Technology in Migration
Technology plays a crucial role in shaping migration trends. From social media platforms that connect migrants with potential employers to digital tools that facilitate the application process for visas, technology has transformed how people migrate. Additionally, data analytics can help governments better understand migration patterns and plan accordingly.
However, reliance on technology also raises concerns about privacy and security. Policymakers must navigate these challenges while leveraging technology to improve the migration experience for all parties involved.
Future Trends in Global Migration
As the world continues to evolve, so too will migration trends. Factors such as climate change, geopolitical shifts, and economic disparities will shape the future of global migration. Understanding these trends is essential for anticipating demographic changes and preparing for their implications.
Future migration patterns may see increased movement towards regions less affected by climate change, as well as shifts in the demographics of migrants themselves. Policymakers must remain adaptable and proactive in addressing the challenges and opportunities that arise from these evolving trends.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition of Migration | Migration refers to the movement of people from one place to another, often across borders, for various reasons including economic opportunities, conflict, and environmental factors. |
| Current Trends | Recent years have seen an increase in both voluntary and forced migration, with significant numbers of people moving due to war, persecution, and climate change. |
| Demographic Changes | Migration affects population size, age structure, and ethnic composition, leading to more diverse societies and changing labor markets. |
| Economic Impact | Migrants contribute to the economy by filling labor shortages, paying taxes, and driving innovation, but can also create challenges in terms of integration and resource allocation. |
| Social Implications | Increased migration can lead to cultural exchange and enrichment, but may also result in social tensions and challenges related to identity and belonging. |
| Policy Responses | Governments are implementing various policies to manage migration, including border control, integration programs, and international cooperation to address root causes. |
| Future Outlook | As global challenges such as climate change and geopolitical conflicts persist, migration trends are likely to continue evolving, necessitating adaptive policies and international collaboration. |