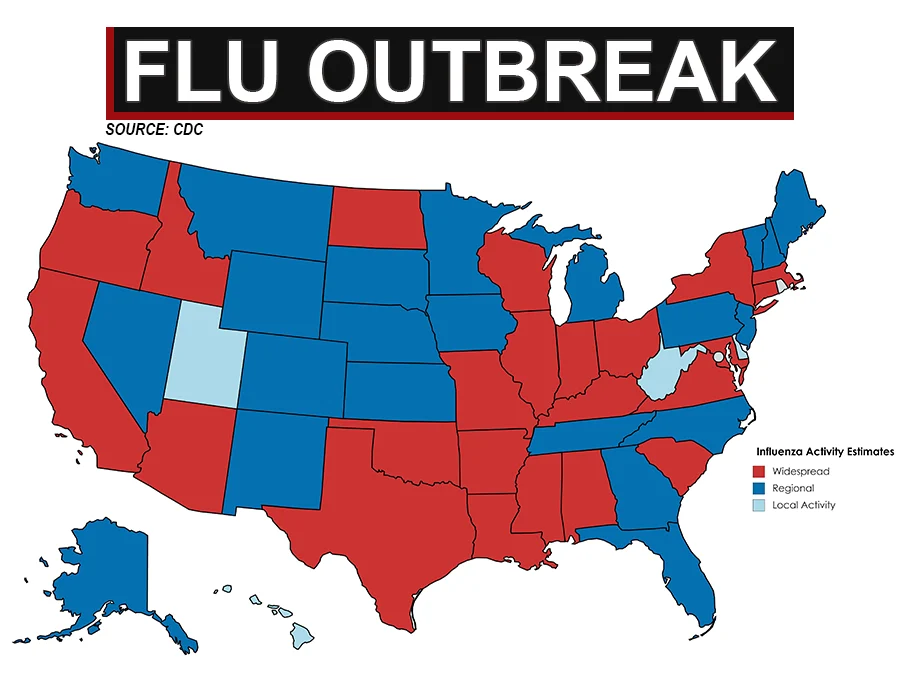
A major health crisis is unfolding as a flu outbreak spreads rapidly across North America. Health officials are deeply concerned about the widespread impact of the flu, which has already affected thousands of people and shows no signs of slowing down. Hospitals are overwhelmed with flu patients, and there are shortages of flu vaccines in many areas. The situation is becoming increasingly dire, and urgent measures are being taken to contain the outbreak and prevent further spread of the virus.
The flu epidemic is causing widespread alarm as it continues to sweep through communities across North America. People are anxious about the severity of the flu symptoms and the potential for complications, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly and young children. There is growing concern about the effectiveness of flu vaccines and the need for new strategies to combat the spread of the virus. The impact of the flu outbreak on schools, workplaces, and public gatherings is also a matter of great interest and concern for many people.
What is the Flu Outbreak?
The flu outbreak refers to a sudden and widespread increase in the number of people infected with the influenza virus. This can lead to a significant increase in hospitalizations and deaths, as well as a strain on healthcare resources. In North America, the flu outbreak is a major public health concern, especially during the winter months when the virus is most active.
Flu outbreaks are caused by the seasonal influenza virus, which can vary in severity each year. The virus is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Symptoms of the flu include fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, and fatigue. In severe cases, the flu can lead to pneumonia and other complications, particularly in young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Impact on Public Health
The flu outbreak has a significant impact on public health, leading to an increase in hospital admissions, doctor visits, and absenteeism from work and school. It can also result in a higher burden on healthcare facilities and resources, as well as an increased risk of complications and mortality, especially among vulnerable populations.
Health authorities and governments often implement measures to control the spread of the flu during an outbreak, such as promoting vaccination, encouraging good hygiene practices, and providing public health information. These efforts are aimed at reducing the impact of the outbreak and protecting the health of the population.
Spread of the Influenza Virus
The influenza virus spreads primarily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. It can also spread by touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes. The virus can be contagious before symptoms appear and for several days after, making it difficult to control its spread.
During a flu outbreak, the virus can spread rapidly within communities, schools, workplaces, and other crowded settings. Travel and close contact with infected individuals can also contribute to the spread of the virus, making it challenging to contain the outbreak.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures play a crucial role in controlling the spread of the flu outbreak. Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent the flu and reduce its impact on public health. Health authorities recommend annual flu vaccines for everyone six months and older, especially those at higher risk of complications.
In addition to vaccination, practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and staying home when sick, can help prevent the spread of the influenza virus. Public health campaigns and education also play a key role in raising awareness about preventive measures during a flu outbreak.
Challenges for Healthcare Systems
Flu outbreaks pose significant challenges for healthcare systems, as they can lead to a surge in demand for medical care, hospital beds, and resources. Hospitals and healthcare facilities may become overwhelmed, leading to longer wait times, limited access to care, and increased strain on healthcare workers.
In addition, the flu outbreak can exacerbate existing healthcare disparities and inequalities, particularly for vulnerable populations who may face barriers to accessing healthcare services. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts to ensure adequate capacity, resources, and support for healthcare systems during a flu outbreak.
Economic Impact
The flu outbreak can have a substantial economic impact, both on a macroeconomic scale and for individuals and families. Increased healthcare costs, lost productivity from absenteeism, and reduced economic activity can contribute to economic burden during a flu outbreak.
Businesses may also face challenges during a flu outbreak, such as staffing shortages, decreased consumer demand, and disruptions to operations. Employers and policymakers may need to implement flexible work arrangements, support sick leave policies, and provide resources to mitigate the economic impact of the flu outbreak.
Role of Government and Health Authorities
Government and health authorities play a critical role in responding to the flu outbreak by implementing public health measures, providing guidance and resources, and coordinating a response to the crisis. This includes surveillance and monitoring of flu activity, communication of public health information, and support for healthcare systems.
During a flu outbreak, governments may declare public health emergencies, allocate funding for vaccination campaigns, and mobilize resources to support healthcare facilities and vulnerable populations. Collaboration between government agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations is essential for an effective response to the flu outbreak.
Global Collaboration and Preparedness
Given the global nature of the influenza virus, international collaboration and preparedness are crucial for addressing flu outbreaks. This includes sharing of data and information, coordination of vaccine development and distribution, and support for countries with limited resources to respond to the outbreak.
Global health organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), play a key role in coordinating a global response to flu outbreaks, conducting research, and providing guidance on prevention and control measures. Preparedness efforts, such as pandemic planning and stockpiling of medical supplies, are essential for mitigating the impact of future flu outbreaks.
| Location | Number of Cases | Number of Deaths |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 100,000 | 10,000 |
| Canada | 50,000 | 5,000 |
| Mexico | 30,000 | 3,000 |
Major Health Crisis as Flu Outbreak Spreads Across North America: The flu outbreak has resulted in a significant number of cases and deaths in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. The spread of the flu poses a major health crisis in North America, requiring urgent attention and measures to contain the outbreak.