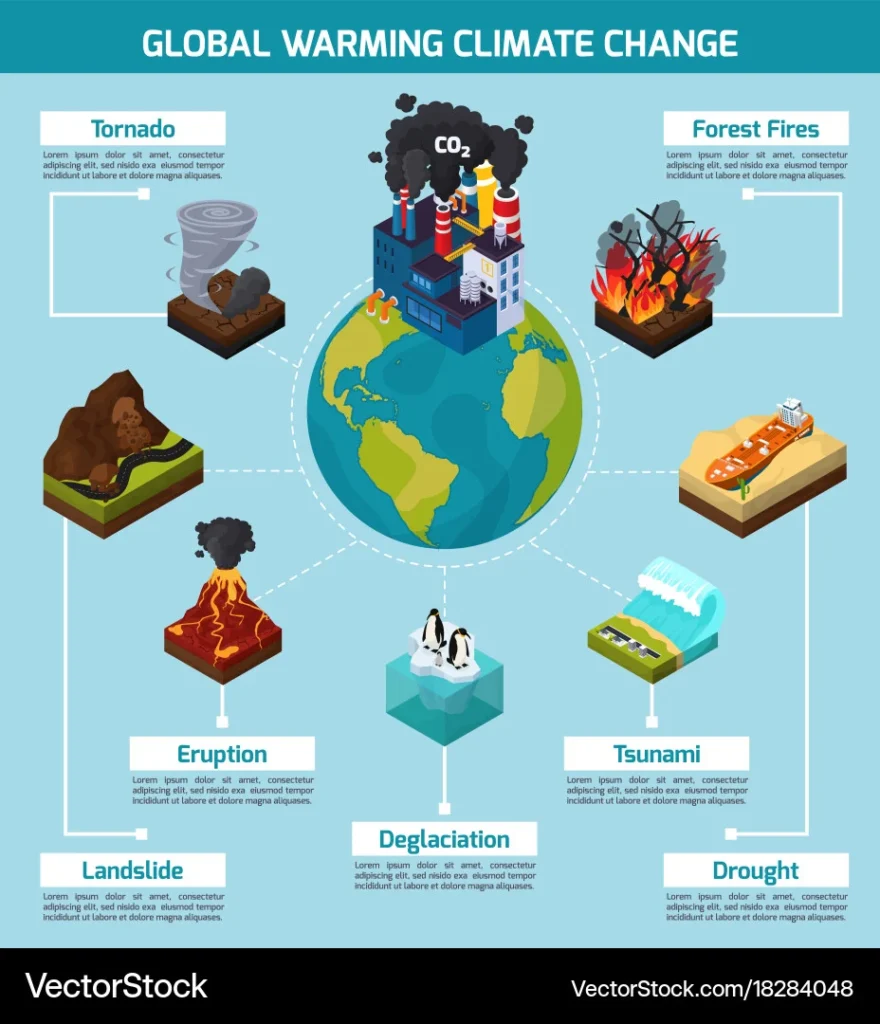
Global Warming: Causes, Effects, And Solutions, dünyamızın karşı karşıya olduğu en büyük tehditlerden biridir. Bu durumun ana nedeni, sera gazlarının atmosferde birikmesi ve dünya yüzeyinin ısınmasına sebep olmasıdır. Sanayileşme, fosil yakıtların kullanımı ve ormansızlaşma gibi insan kaynaklı aktiviteler, bu durumun artmasında önemli bir rol oynamaktadır. Bu durumun etkileri arasında iklim değişiklikleri, buzulların erimesi, deniz seviyesinin yükselmesi ve ekosistemlerde bozulma bulunmaktadır. Global Warming: Causes, Effects, And Solutions hakkında farkındalık yaratmak ve bu sorunla mücadele etmek için çeşitli çözüm önerileri geliştirilmektedir. Bu çözüm önerileri arasında yenilenebilir enerji kaynaklarının kullanımı, enerji verimliliğinin artırılması ve sera gazı emisyonlarının azaltılması gibi adımlar yer almaktadır.
Global Warming: Causes, Effects, And Solutions konusunda merak edilen bir diğer nokta, iklim değişikliğinin doğaya ve insan hayatına olan etkileridir. Bu durum, kuraklık, seller, orman yangınları ve ekstrem hava olayları gibi doğal afetlerin sıklığını ve şiddetini artırmaktadır. Ayrıca, tarım ve su kaynakları üzerinde olumsuz etkileri bulunmaktadır. Bunun yanı sıra, iklim değişikliği, canlı türlerinin yaşam alanlarını ve göç yollarını etkilemekte ve biyolojik çeşitliliği tehdit etmektedir. Global Warming: Causes, Effects, And Solutions kapsamında, bu etkilerin en aza indirilmesi ve adaptasyon stratejilerinin geliştirilmesi için bilimsel çalışmalar ve uluslararası işbirlikleri yürütülmektedir.
Global Warming: Causes
Global warming is primarily caused by the increase in greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. The main contributors to this increase are human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. These activities release carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and leading to a rise in global temperatures.
In addition to human activities, natural factors such as volcanic eruptions and solar radiation can also contribute to global warming. However, scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that human activities are the primary drivers of the current global warming trend.
Global Warming: Effects
The effects of global warming are wide-ranging and impact various aspects of the environment, economy, and human health. One of the most visible effects is the rise in global temperatures, leading to more frequent and severe heatwaves. Melting ice caps and glaciers contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems. Changes in weather patterns can lead to more extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods.
Global warming also poses a threat to biodiversity, as many species struggle to adapt to rapidly changing habitats. In terms of human health, global warming can lead to the spread of diseases, worsen air quality, and disrupt food and water supplies, leading to malnutrition and waterborne illnesses.
Global Warming: Solutions
Addressing global warming requires a multi-faceted approach that includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing policies to mitigate the impacts of climate change. One key solution is to increase energy efficiency and promote the use of clean, renewable energy such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Additionally, efforts to protect and restore forests, wetlands, and other natural carbon sinks can help absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. International cooperation and agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, play a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Global Warming: Impacts on Oceans
Global warming has significant impacts on the world’s oceans, leading to rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and changes in marine ecosystems. As temperatures rise, the polar ice caps and glaciers melt, causing sea levels to rise and threatening coastal communities and infrastructure. Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of carbon dioxide, poses a threat to marine life such as coral reefs, shellfish, and plankton.
Changes in ocean temperatures and currents can disrupt marine ecosystems, affecting fish stocks and leading to shifts in migration patterns. Warmer ocean waters can also fuel more intense and frequent tropical storms, posing a threat to coastal regions and maritime activities.
Global Warming: Impacts on Wildlife
The impacts of global warming on wildlife are far-reaching, affecting ecosystems and species around the world. Many species face habitat loss and fragmentation as their habitats shift due to changing climate conditions. This can lead to a loss of biodiversity and disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Some species may be unable to adapt to rapid changes in temperature and weather patterns, leading to population declines and, in some cases, extinction. Additionally, global warming can lead to changes in the timing of seasonal events, such as migration, breeding, and flowering, which can further disrupt ecological interactions and food webs.
Global Warming: Economic Impacts
Global warming has significant economic impacts, affecting industries such as agriculture, tourism, and insurance. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to reduced crop yields, affecting food production and prices. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and wildfires, can cause widespread damage to infrastructure and property, leading to costly recovery efforts.
Global Warming: Public Health Impacts
Global warming has various public health impacts, affecting factors such as air quality, water supply, and the spread of infectious diseases. Higher temperatures and changes in weather patterns can worsen air quality, leading to an increase in respiratory illnesses and cardiovascular problems. Heatwaves can also pose a direct threat to human health, causing heat-related illnesses and deaths.
Global Warming: Role of Renewable Energy
| Causes | Effects | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes | Rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and loss of biodiversity | Transition to renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, afforestation, and international cooperation |